The history of cybersecurity is a fascinating journey that reflects the ongoing battle between digital attackers and defenders. It traces back to the earliest attempts to safeguard digital systems from malicious intrusions.
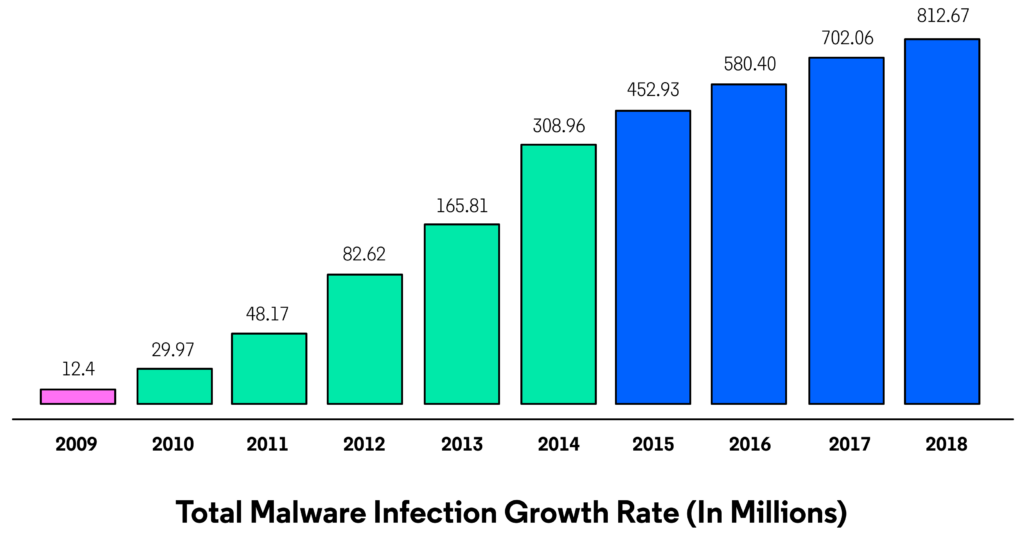
Over the decades, cybersecurity has evolved in tandem with advancements in technology and the emergence of new threats. From the rudimentary defenses of the 1960s to the sophisticated strategies of the present day, the landscape of cybersecurity has been shaped by a constant arms race between cybercriminals and security professionals.
In the modern era, the proliferation of digital data and the increasing reliance on interconnected systems have heightened the importance of cybersecurity. With laws and regulations mandating the protection of sensitive information, organizations are held accountable for safeguarding data privacy. This has led to the development of industry standards and frameworks, as well as the implementation of security measures tailored to specific sectors such as healthcare and finance.
Amidst these challenges, the concept of Zero Trust security has emerged as a paradigm shift in cybersecurity philosophy. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on perimeter-based defenses, Zero Trust operates on the principle of never trusting, always verifying. This means that every user and device accessing resources on a network must undergo strict identity verification, regardless of their location or status within the network.
Key principles of Zero Trust include:
- Continuous monitoring and validation
- Least privilege access
- Device access control
- Micro segmentation
- Preventing lateral movement
- Multi-factor authentication
By adhering to these principles, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and minimize the impact of security breaches.

The adoption of Zero Trust has gained momentum in recent years, driven by the increasing complexity of cyber threats and the need for more robust security measures. Major continuous monitoring and validation least privilege access device access control micro segmentation preventing lateral movement multi-factor authentication. organizations, including tech giants like Google, have embraced Zero Trust as a core component of their cybersecurity strategy. Additionally, industry analysts and research firms have recognized Zero Trust as a vital approach to network security in the modern digital landscape.
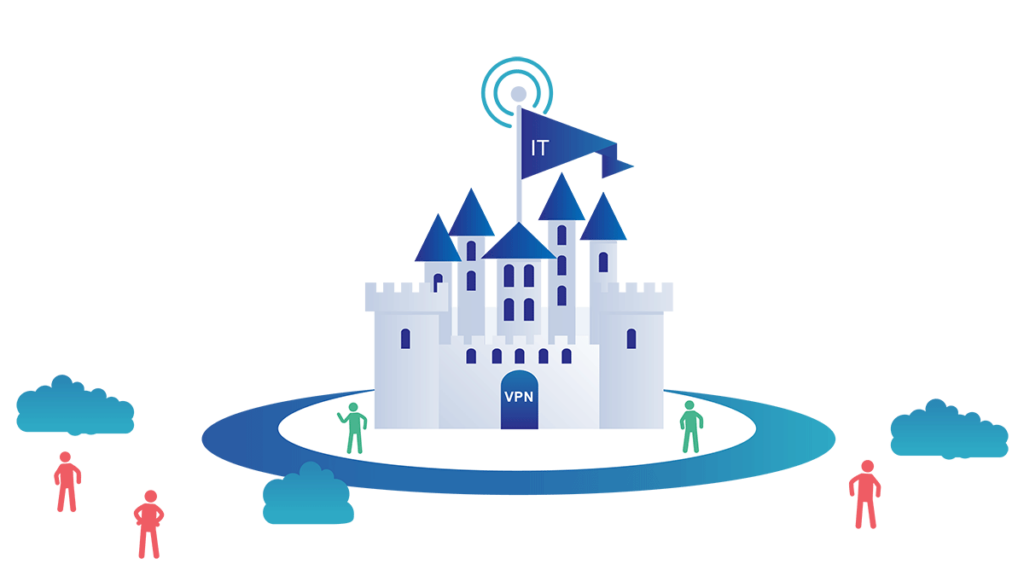

Implementing Zero Trust security requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses both technology and organizational practices. Platforms like Cloudflare One offer integrated solutions that combine networking services with Zero Trust principles, making it easier for organizations to transition to this security model. By embracing Zero Trust, organizations can enhance their security posture, reduce their exposure to cyber threats, and safeguard their valuable data assets in an increasingly interconnected world.
