In today’s world, network security is a vital component of cybersecurity. Organizations rely heavily on network security systems to protect their sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Among the most critical instruments in these mechanisms are firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). In this blog, we’ll explore what these tools are, how they work, and their importance in safeguarding networks
What is Network Security?
Network security are a set of policies, (best) practices, and technologies designed to ensureing the confidentiality, integrity and availability (CIA) of an organization’s network and data. Which translates to preventing unauthorized access, misuse, or disruption of network resources.
Firewalls: The First Line of Defense
What is a Firewall?
- A firewall is a network security mechanism, either in hardware or software, that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a (secure) trusted internal network and a pottentialy harmful untrusted external networks, such as the internet.
How Firewalls Work
- Packet Filtering: Firewalls analyze data packets based on source/destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. Any packet that doesn’t meet the firewall’s security rules, is blocked.
- Stateful Inspection: Unlike basic packet filtering, stateful firewalls keep track of the status of active connections. They can determine whether a packet is part of an established connection or an unauthorized attempt.
- Proxy Service: Some firewalls function as intermediaries by accepting requests from clients and forwarding them to the intended server. This process adds an extra layer of security by hiding the internal network.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): These advanced firewalls offer additional features such as application-layer inspection, intrusion prevention, and advanced threat detection.
Why Firewalls Matter
- Protect Against Unauthorized Access: Firewalls block malicious traffic from entering your network.
- Prevent Data Exfiltration: They also help in ensuring sensitive data does not leave the network without authorization.
- Enhance Network Segmentation: By controlling traffic between different parts of the network, firewalls help minimize the spread of malware or lateral movement by attackers.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Detecting Threats in Real-Time
What is an IDS?
An Intrusion Detection System is a security tool designed to detect unauthorized access or suspicious activities within a network. Unlike firewalls that prevent harmful traffic, an IDS is dedicated to monitoring activities and generating alerts.
Types of IDS
- Network-Based IDS (NIDS): These systems monitor network traffic for signs of malicious activity. They are typically placed at key points within the network, such as between the firewall and internal network.
- Host-Based IDS (HIDS): These are installed on individual devices to monitor activity like file changes, application behavior, and system logs.
How IDS Works
- Signature-Based Detection: The IDS uses a database of known attack patterns (signatures) to identify threats. For example, it might recognize a sequence of packets as a DDoS attack.
- Anomaly-Based Detection: The system learns normal network behavior over time and alerts the administrator when it detects deviations from this baseline.
- Hybrid Detection: Combines signature-based and anomaly-based methods for improved accuracy.
Why IDS is Important
- Early Threat Detection: IDS can identify threats in real-time, enabling faster response.
- Incident Investigation: IDS logs provide valuable insights during forensic analysis after an incident.
- Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks require organizations to monitor network activity and detect intrusions.
Firewalls vs. IDS: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Firewall | IDS |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Blocks unauthorized traffic | Monitors and detects suspicious activity |
| Action | Preventive | Detective |
| Deployment | At network entry/exit points | Inside the network |
| Focus | Traffic filtering and access control | Threat detection and alerting |
| Response | Automatically blocks unauthorized traffic | Alerts administrators to take action |
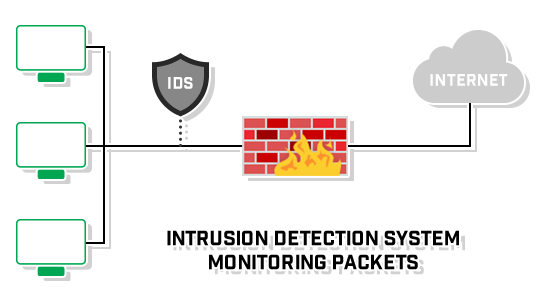
The Importance of Using Both
While firewalls and IDS serve different purposes, they complement each other. A firewall prevents known threats from entering the network, while an IDS detects sophisticated attacks that might bypass the firewall or originate from inside the network. Together, they provide a robust defense against a wide range of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Understanding how firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems work is fundamental for anyone in cybersecurity. These tools are critical components of a comprehensive network security strategy, helping organizations protect their assets and respond to threats effectively.
